Today's task: verifying that a Keydb cluster, when deployed via Helm with default values (apart from activating LoadBalancer Service and a custom password), could be resilient to the sudden death of any one of its composing Pods, with no client connection's disruption.
Also today's task: learn to interact with Redis/Keydb via Python.
References
- Codeberg GIT repo for this project: https://codeberg.org/rimmon1971/kind-python-keydb
-
Kubie multicontext manager: https://github.com/sbstp/kubie
-
KeyDB Redis replacement: https://docs.keydb.dev/
-
KeyDB Helm Chart: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/enapter/keydb
-
Using Python to interact with Redis: https://realpython.com/python-redis/
-
Best practices for Redis clients: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/database/best-practices-redis-clients-and-amazon-elasticache-for-redis/
-
How to setup HAProxy for Sentinel on Kubernetes: https://yaniv-bhemo.medium.com/how-to-setup-haproxy-for-redis-sentinel-on-kubernetes-37ee70e44464
Reusing an existing, test, AKS cluster
Here we are:
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ az aks list -o table
Name Location ResourceGroup KubernetesVersion CurrentKubernetesVersion ProvisioningState Fqdn
------ ------------- ------------------------ ------------------- -------------------------- ------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------
keydb francecentral DefaultResourceGroup-PAR 1.23.12 1.23.12 Succeeded keydb-defaultresourceg-f1fbee-d3388059.hcp.francecentral.azmk8s.io
Let's extract the related kubeconfig file
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ az aks get-credentials --admin --name keydb --resource-group DefaultResourceGroup-PAR --file ~/.kube/keydb.yml
The behavior of this command has been altered by the following extension: aks-preview
Merged "keydb-admin" as current context in /home/ferdi/.kube/keydb.yml
And making use of that, via Kubie multi-context manager.
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ sed -i 's/keydb-admin/keydb/g' /home/ferdi/.kube/keydb.yml
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ kubie ctx keydb
[keydb|default] ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
aks-nodepool1-21172355-vmss000000 Ready agent 18d v1.23.12
aks-nodepool1-21172355-vmss000001 Ready agent 18d v1.23.12
aks-nodepool1-21172355-vmss000002 Ready agent 18d v1.23.12
Installing Keydb cluster with default values (except for a password)
First of all, we need to add Keydb's Helm repo:
[kind|default] ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ helm repo add enapter https://enapter.github.io/charts/
"enapter" has been added to your repositories
Now we can perform a multi-master, active replica, three node Keydb cluster installation (with our carefully chosen password). Discovering what does our password mean is left as an exercise for the reader :-)
[kind|default] ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ helm upgrade --install keydb enapter/keydb --set password="Savignone.2015" --set loadBalancer.enabled=true
Release "keydb" does not exist. Installing it now.
NAME: keydb
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 21 11:15:06 2022
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
Reaching it
We're going to run our Python code from the local PC, so we need to discover the Public IP through which our Keydb cluster is exposed.
[keydb|default] ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
keydb ClusterIP 10.0.137.22 <none> 6379/TCP,9121/TCP 19m
keydb-headless ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP 19m
keydb-lb LoadBalancer 10.0.74.115 EDITED 6379:31052/TCP 19m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 18d
Redis cluster support with Python
The go-to Python library redis-py to interact with Redis used to lack cluster support. In 2022, AWS people added this functionality (previously you had to choose another library to work with Redis clusters) to redis-py, as described here. However, when using this library against a KeyDB cluster, you should not instantiate a RedisCluster object: you should use the plain-and-simple Redis object, letting the internal KeyDB synchronization mechanism to work with your data. There is also a KeyDB-specific Python library but its development seems to have stopped 3 years ago.
A Python virtualenv
I'm assuming that your Linux environment already has Python (3.7+) installed, along with the customary python3-venv, python3-setuptools, python3-wheel packages. Let's create our virtual environment and proceed to install the Redis client library there.
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ python3 -m venv env
ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ . env/bin/activate
(env) ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ pip install redis
Collecting redis
Downloading redis-4.3.4-py3-none-any.whl (246 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 246 kB 2.7 MB/s
Collecting async-timeout>=4.0.2
Using cached async_timeout-4.0.2-py3-none-any.whl (5.8 kB)
Collecting deprecated>=1.2.3
Downloading Deprecated-1.2.13-py2.py3-none-any.whl (9.6 kB)
Collecting packaging>=20.4
Using cached packaging-21.3-py3-none-any.whl (40 kB)
Collecting wrapt<2,>=1.10
Downloading wrapt-1.14.1-cp38-cp38-manylinux_2_5_x86_64.manylinux1_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (81 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 81 kB 8.5 MB/s
Collecting pyparsing!=3.0.5,>=2.0.2
Using cached pyparsing-3.0.9-py3-none-any.whl (98 kB)
Installing collected packages: async-timeout, wrapt, deprecated, pyparsing, packaging, redis
Successfully installed async-timeout-4.0.2 deprecated-1.2.13 packaging-21.3 pyparsing-3.0.9 redis-4.3.4 wrapt-1.14.1
(env) ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ pip freeze > requirements.txt
(env) ferdi@DESKTOP-NL6I2OD:~/kind-python-keydb$ cat requirements.txt
async-timeout==4.0.2
Deprecated==1.2.13
packaging==21.3
pyparsing==3.0.9
redis==4.3.4
wrapt==1.14.1
Poor man's Redis reader and writer
The goal is to verify the resilience of a KeyDB cluster, so there's nothing fancy in the code, apart from the retry_with_backoff function shamelessly stolen from the Best Practices's AWS link.
library.py
import redis
import random
from time import sleep
from redis.exceptions import ConnectionError, TimeoutError
def run_with_backoff(function, retries=5):
base_backoff = 0.1
max_backoff = 10
tries = 0
while True:
try:
return function()
except (ConnectionError,TimeoutError):
if tries >= retries:
raise
backoff = min(max_backoff, base_backoff * (pow(2, tries) + random.random()))
print(f"sleeping for {backoff:.2f}s")
sleep(backoff)
tries += 1
writer.py
from library import *
random.seed(444)
pool = redis.BlockingConnectionPool(host='EDITED',port='6379',password='Savignone.2015',decode_responses=True)
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
while True:
for i in range(1000):
valore = random.getrandbits(64)
rs = run_with_backoff(lambda: r.set(f"chiave{i}",valore))
print(f"{i} {valore} {rs}")
reader.py
from library import *
random.seed(555)
pool = redis.BlockingConnectionPool(host='EDITED',port='6379',password='Savignone.2015',decode_responses=True)
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
while True:
chiave = random.randint(0,999)
valore = run_with_backoff(lambda: r.get(f"chiave{chiave}"))
print(f"{chiave} {valore}")
First results
I launched both reader.py and writer.py from within the virtual environment, and I noticed that often, deleting one of the Pods part of the KeyDB StatefulSet, my client's connection was interrupted (and therefore the retry mechanism kicked in).
The customer, however, reads and writes Redis data in a way that doesn't tolerate connectivity loss.
So, next step: remove LoadBalancer Service from KeyDB (actually, I'm lazy, I'm letting it in place for now) and put HAProxy in front of it, exposing the proxy instead.
Putting HAProxy at work
First of all: kudos to Yaniv Ben Hemo for putting it simple with HAProxy on Kubernetes: relying on Kubernetes' DNS capabilities to resolve the individual KeyDB Pod's IP addresses is effective.
I've modified only the ConfigMap to reflect the fact that KeyDB is multi-master active-replica by default, and thus the writes can be distributed freely on each active backend node.
Additionally, I'm looking for role:active-replica and not role:master for the same reason.
Below there's a screenshot of HAProxy's stats page taken when I went berserk and killed two out of three KeyDB pods. Both reader and writer Python scripts never noticed (after having been pointed to the new* public IP).
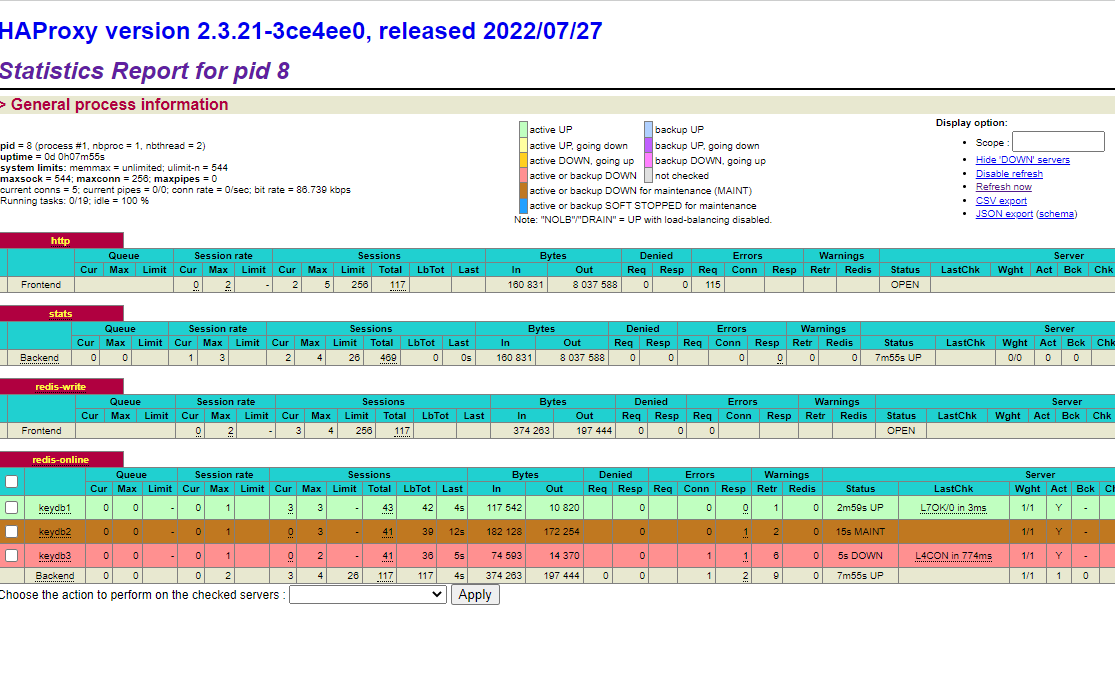
And then, the complete YAML (Service, ConfigMap, Deployment) for our marvellous HAProxy.
apiVersion: /v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: haproxy-service
namespace: default
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: dashboard
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
- name: redis-write
port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
selector:
app: haproxy
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: haproxy-config
namespace: default
data:
haproxy.cfg: |
global
daemon
maxconn 256
defaults
mode tcp
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
frontend http
bind :8080
default_backend stats
backend stats
mode http
stats enable
stats enable
stats uri /
stats refresh 1s
stats show-legends
stats admin if TRUE
resolvers k8s
parse-resolv-conf
hold other 10s
hold refused 10s
hold nx 10s
hold timeout 10s
hold valid 10s
hold obsolete 10s
frontend redis-write
bind *:6379
default_backend redis-online
backend redis-online
mode tcp
balance roundrobin
option tcp-check
tcp-check send AUTH\ Savignone.2015\r\n
tcp-check expect string +OK
tcp-check send PING\r\n
tcp-check expect string +PONG
tcp-check send info\ replication\r\n
tcp-check expect string role:active-replica
server-template keydb 3 server._tcp.keydb-headless.default.svc.cluster.local:6379 check inter 1s resolvers k8s init-addr none
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: haproxy-deployment
namespace: default
labels:
app: haproxy
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: haproxy
template:
metadata:
name: haproxy-pod
labels:
app: haproxy
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- haproxy
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
containers:
- name: haproxy
image: haproxy:2.3
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
- containerPort: 6379
- containerPort: 6380
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /usr/local/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
subPath: haproxy.cfg
readOnly: true
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: haproxy-config